Accumulated Earnings Tax C Corporation
In 2020, the corporation made a net. The rules governing distributions from c corporations differ from the rules that apply to distributions from s corporations.

Income Tax Computation For Corporate Taxpayers Prepared By
A) in practice, the accumulated earnings tax applies only to closely held corporations.

Accumulated earnings tax c corporation. Because a corporation is a taxable entity that is separate from its stockholders, its excess profits (profits remaining after being taxed at the corporate level) are not, as in the case of unincorporated businesses and s. For c corporations, the current accumulated retained earnings threshold that triggers this tax is $250,000. The base for the accumulated earnings penalty is accumulated taxable income.
The accumulated earnings tax imposed by section 531 shall apply to every corporation (other than those described in subsection (b)) formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders or the shareholders of any other corporation, by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed. Publicly held corporations with many. New corp is an s corporation that has subchapter c accumulated earnings and profits of $20,000 on december 31, 2019, the day it converted to an s corporation.
Accumulated tax earning is a form of encouragement by the government to give out dividends, rather than keeping their earnings. If a corporation pursues an earnings accumulation strategy, where the accumulation is to avoid the tax on dividends rather than having a business purpose, then irc §532 provides an accumulated earnings tax that can be assessed on accumulated earnings with no clear business purpose. These factors somewhat mute the apparent advantage of the lower corporate rate.
A corporation can accumulate its earnings for a possible expansion or other bona fide business reasons. There is a certain level in which the. The aet is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings.
It is a form of tax imposed by the federal government on firms and cooperation with retained earnings. Not taking a returns usually makes good sense for new or small businesses where the money is being reinvested right into expanding procedures. To the extent that a distribution is made from the corporation’s earnings and profits, it.
This is because corporations that do not spend retained earnings are generally more valuable than those without accumulated retained earnings. C corp accumulated earnings tax if business owners are only taking a salary, that amount is not tired at the business rate changing the tax equation even more in their favor. An accumulated earnings tax is a tax imposed by the federal government on companies with retained earnings deemed to be unreasonable and in excess of what is considered ordinary.
Accumulated e&p was taxed at the c corporation level and will be taxed again as a dividend to recipient s corporation shareholders when distributed. As shown in the following table, under the new individual income tax rate structure, the top bracket is reached at $600,000 for a married taxpayer filing jointly (mfj) for the 2018 tax year. B) a corporation bears the burden of proving that its earnings are not being accumulated to avoid income taxes.
The accumulated earnings tax is an annual tax levied on modified taxable income (sec. This gives very little leeway for c corporations to pay the 21% tax and build up savings without dividends unless there are provable business needs to accumulate more. It is calculated in a similar way to retained earnings, but the two amounts are.
However, if a corporation allows earnings to accumulate beyond the reasonable needs of the business, it may be subject to. The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the irs, typically during an irs audit. S corporations that have accumulated.
A corporation's earnings and profits (e&p) is the measure of its ability to pay dividends for income tax purposes. A taxable dividend is defined as a distribution from current or accumulated earnings and profits (e&p) of the distributing corporation (computed at the end of the year). C) to avoid the accumulated earnings tax, a corporation needs to have a definite plan for expending the accumulated earnings.
535(b)) retained in the business in excess of its reasonable needs. A corporation determines this amount by adjusting its taxable income for “economic items” to better reflect how much cash it has available to make dividend distributions. This earning is considered unreasonable and somewhat unnecessary.
Example of accumulated earnings tax. Company a is a c corporation that deals in selling beverages and is required to pay accumulated earnings tax if it retains more than $250,000 of its earnings. Accumulated e&p refers to sums accumulated prior to the taxable year.
Breaking down accumulated earnings tax. When the aet is assessed, the tax rate is the same as the maximum federal rate on dividends received by individuals. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20%, the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed.
The corporation's accumulated earnings exceed $250,000 (or $150,000 for a personal service corporation), and the corporation can't demonstrate economic need for the excess accumulated earnings.
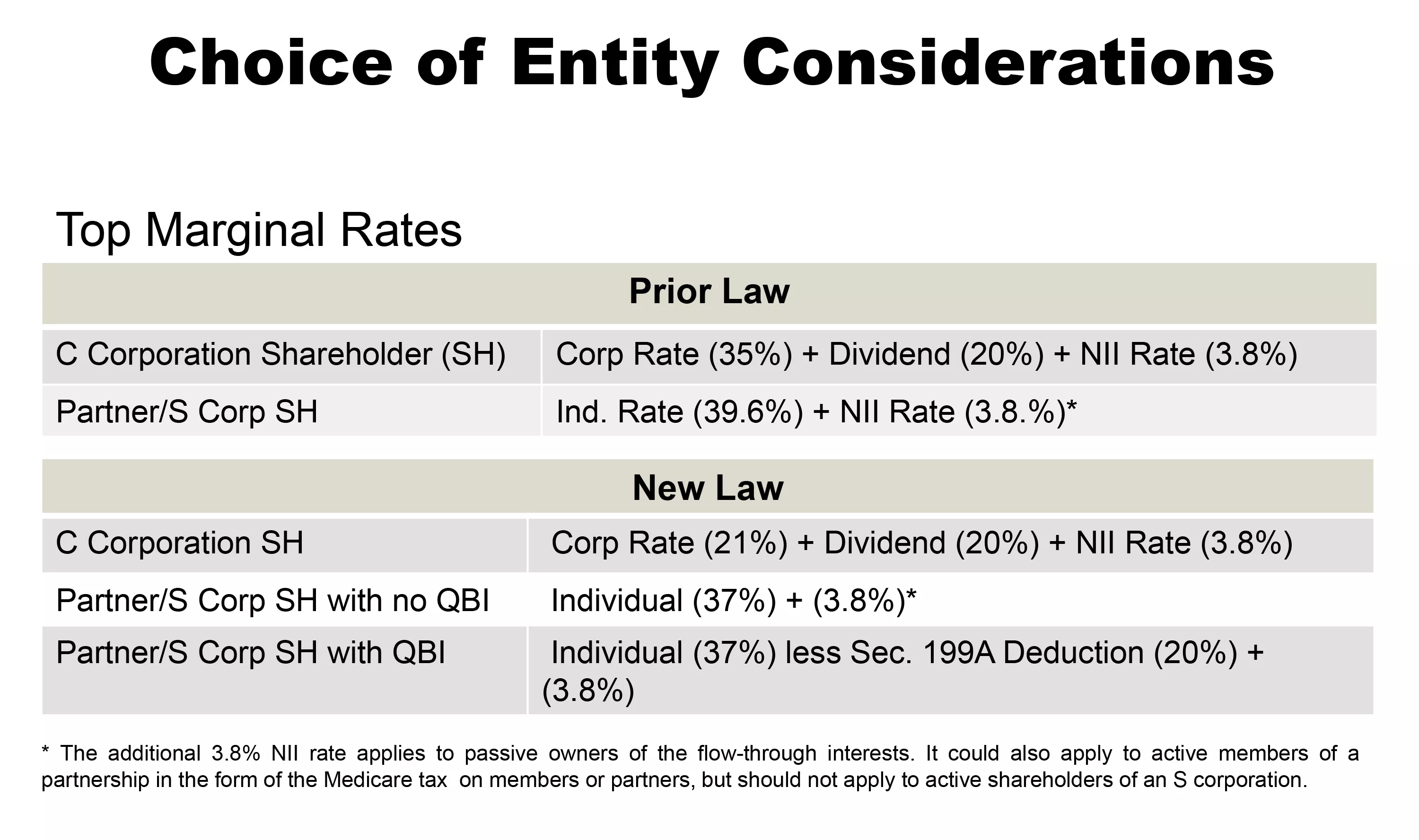
Tax Treatment For C Corporations And S Corporations Under The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act - Smith And Howard - Cpa

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
What Are Accumulated Earnings - Definition Meaning Example

Income Tax Computation For Corporate Taxpayers Prepared By

Strategies For Avoiding The Accumulated Earnings Tax - Krd

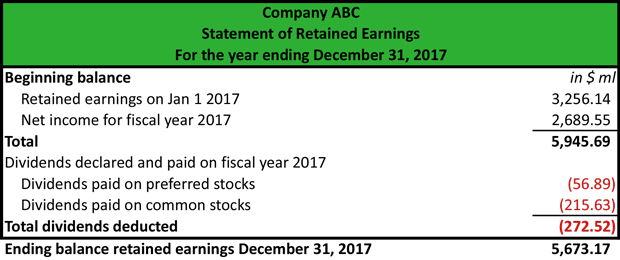
Statement Of Retained Earnings Reveals Distribution Of Earnings Earnings Net Income Dividend

Oh How The Tables May Turn C To S Conversion Considerations Stout

Cares Act Implications On Corporate Earnings And Profits Ep

Chapter 23 - Statement Of Cash Flows Mc Computational Flashcards Quizlet

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
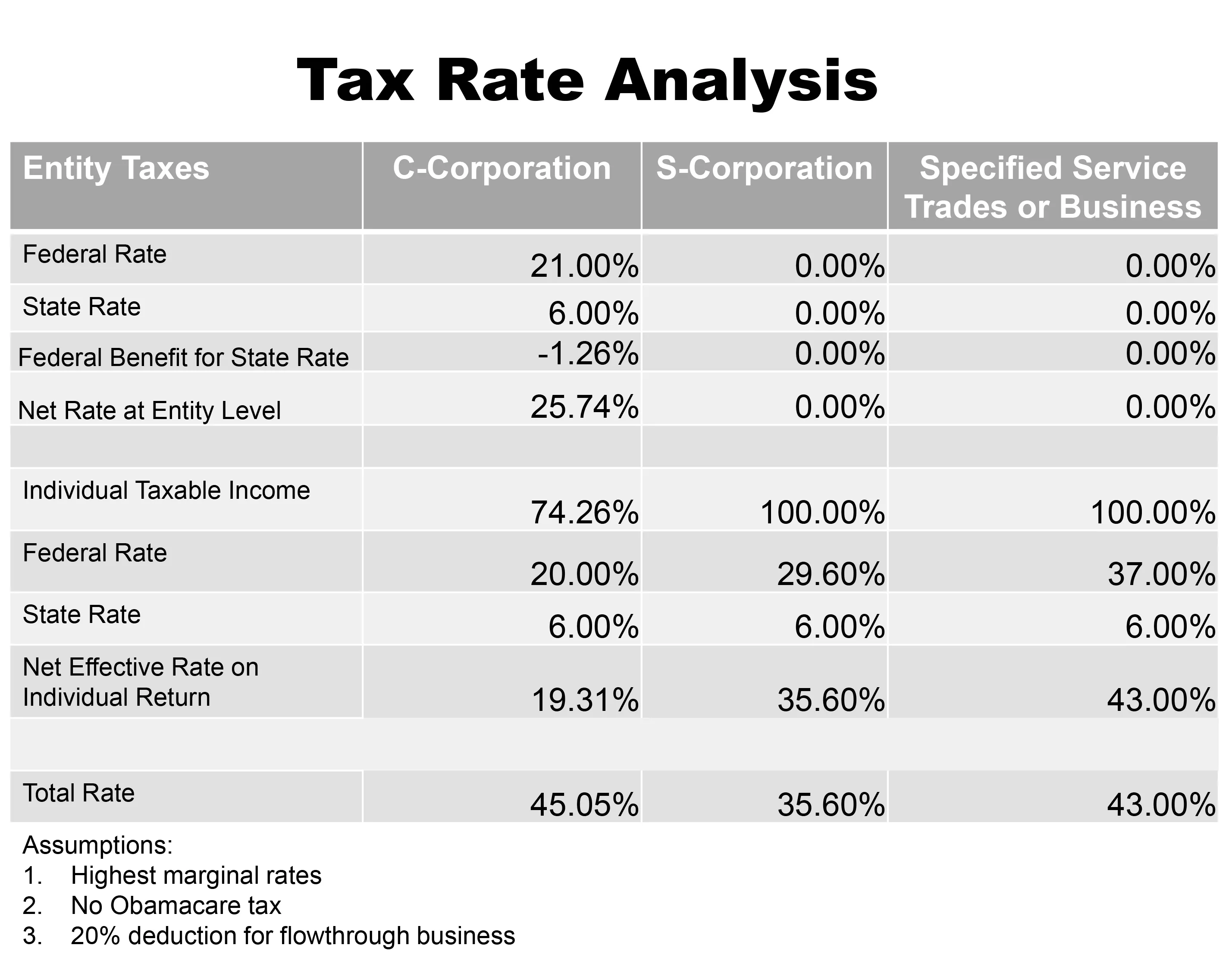
Tax Treatment For C Corporations And S Corporations Under The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act - Smith And Howard - Cpa

Oh How The Tables May Turn C To S Conversion Considerations Stout

Understanding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Before Switching To A C Corporation In 2019

Statement Of Retained Earnings Reveals Distribution Of Earnings Earnings Business Questions Financial Statement
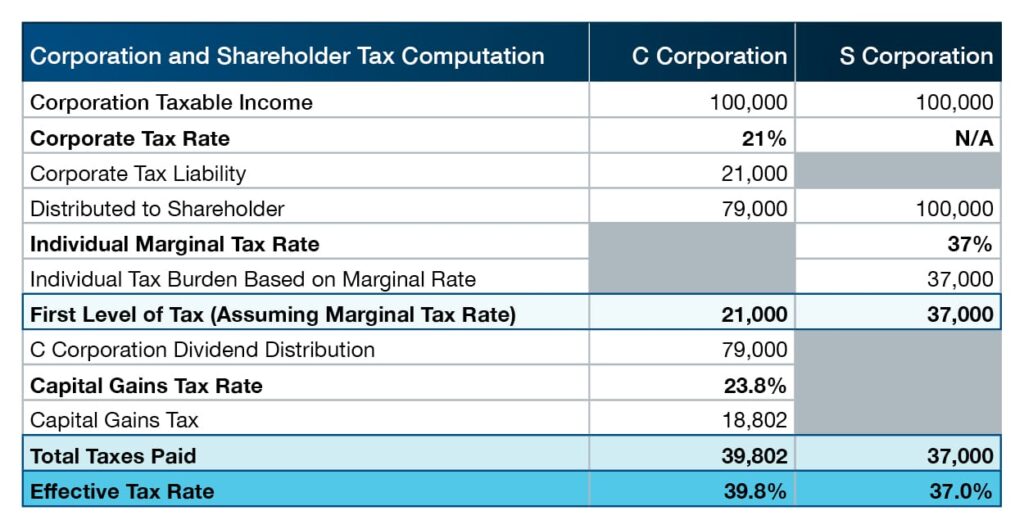
S Corporation Or C Corporation Under The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act - Pya

Irs Use Of Accumulated Earnings Tax May Increase
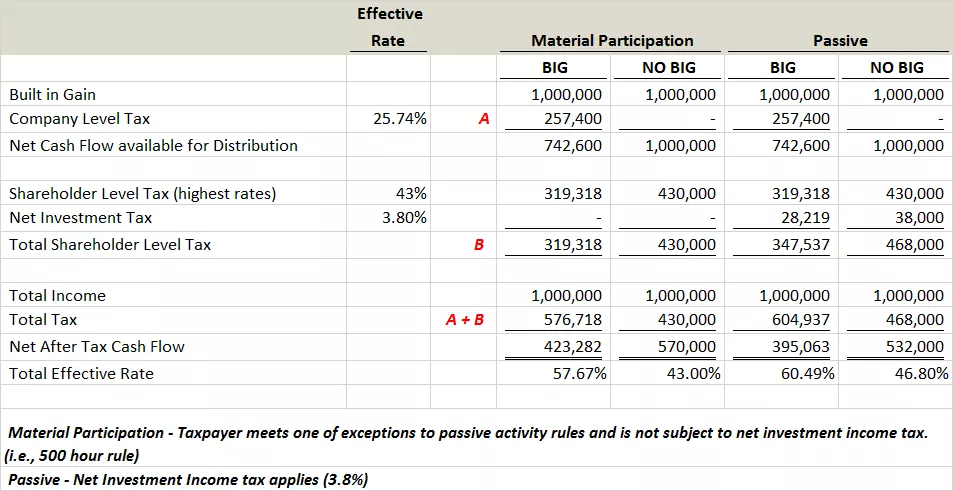
Tax Treatment For C Corporations And S Corporations Under The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act - Smith And Howard - Cpa

Income Tax Computation Corporate Taxpayer 1 2 What Is A Corporation Corporation Is An Artificial Being Created By Law Having The Rights Of Succession - Ppt Download
Solved A How Much Is The Income Tax Due For 2019 Assuming That It Is A Domestic Corporation B How Much Is The Income Tax Due For 2019 Assuming Course Hero